How To Change Rotation Point After Effects
- Later Effects User Guide
- Beta releases
- Beta Program Overview
- After Effects Beta Habitation
- Features in Beta
- Properties panel (Beta)
- Getting started
- Go started with Later on Effects
- What's new in After Effects
- Release Notes | After Effects
- Afterwards Furnishings arrangement requirements
- Keyboard shortcuts in Subsequently Effects
- Supported File formats | After Furnishings
- Hardware recommendations
- After Furnishings for Apple silicon
- Planning and setup
- Setup and installation
- Workspaces
- General user interface items
- Get to know Subsequently Effects interface
- Workflows
- Workspaces, panels, and viewers
- Projects and compositions
- Projects
- Composition basics
- Precomposing, nesting, and pre-rendering
- View detailed performance information with the Composition Profiler
- CINEMA 4D Composition Renderer
- Importing footage
- Preparing and importing still images
- Importing from Afterwards Effects and Adobe Premiere Pro
- Importing and interpreting video and audio
- Preparing and importing 3D image files
- Importing and interpreting footage items
- Working with footage items
- Detect edit points using Scene Edit Detection
- XMP metadata
- Text and Graphics
- Text
- Formatting characters and the Grapheme panel
- Text effects
- Creating and editing text layers
- Formatting paragraphs and the Paragraph panel
- Extruding text and shape layers
- Animating text
- Examples and resources for text animation
- Live Text Templates
- Motion Graphics
- Work with Move Graphics templates in After Furnishings
- Utilize expressions to create drop-down lists in Motion Graphics templates
- Work with Essential Properties to create Motion Graphics templates
- Supercede images and videos in Motion Graphics templates and Essential Properties
- Text
- Drawing, Painting, and Paths
- Overview of shape layers, paths, and vector graphics
- Paint tools: Brush, Clone Postage, and Eraser
- How to taper shape strokes
- Shape attributes, pigment operations, and path operations for shape layers
- Use Showtime Paths shape event to alter shapes
- Creating shapes
- Create masks
- Remove objects from your videos with the Content-Aware Make full panel
- Roto Brush and Refine Matte
- Layers, Markers, and Photographic camera
- Selecting and arranging layers
- Blending modes and layer styles
- 3D layers
- Layer properties
- Creating layers
- Managing layers
- Layer markers and limerick markers
- Cameras, lights, and points of interest
- Blitheness, Keyframes, Motion Tracking, and Keying
- Blitheness
- Animation basics
- Animating with Puppet tools
- Managing and animating shape paths and masks
- Animating Sketch and Capture shapes using Afterwards Effects
- Contrasted blitheness tools
- Work with Data-driven blitheness
- Keyframe
- Keyframe interpolation
- Setting, selecting, and deleting keyframes
- Editing, moving, and copying keyframes
- Move tracking
- Tracking and stabilizing motion
- Face Tracking
- Mask Tracking
- Mask Reference
- Speed
- Time-stretching and time-remapping
- Timecode and time display units
- Keying
- Keying
- Keying effects
- Blitheness
- Transparency and Compositing
- Compositing and transparency overview and resource
- Alpha channels, masks, and mattes
- Adjusting color
- Color basics
- Use the Adobe Color Themes extension
- Colour management
- Color Correction furnishings
- Effects and Animation Presets
- Furnishings and animation presets overview
- Effect list
- Simulation effects
- Stylize effects
- Audio effects
- Distort effects
- Perspective effects
- Channel effects
- Generate effects
- Transition furnishings
- The Rolling Shutter Repair issue
- Blur and Sharpen effects
- 3D Aqueduct effects
- Utility effects
- Matte furnishings
- Noise and Grain effects
- Particular-preserving Upscale effect
- Obsolete effects
- Expressions and Automation
- Expression
- Expression basics
- Understanding the expression linguistic communication
- Using expression controls
- Syntax differences between the JavaScript and Legacy ExtendScript expression engines
- Editing expressions
- Expression errors
- Using the Expressions editor
- Use expressions to edit and access text properties
- Expression language reference
- Expression examples
- Automation
- Automation
- Scripts
- Expression
- Immersive video, VR, and 3D
- Construct VR environments in Later Effects
- Apply immersive video effects
- Compositing tools for VR/360 videos
- Tracking 3D camera motion
- Work in 3D Design Space
- 3D Transform Gizmos
- Do more than with 3D animation
- Preview changes to 3D designs existent time with the Existent-Fourth dimension Engine
- Add responsive pattern to your graphics
- Views and Previews
- Previewing
- Video preview with Mercury Transmit
- Modifying and using views
- Rendering and Exporting
- Basics of rendering and exporting
- Export an Afterwards Effects project equally an Adobe Premiere Pro project
- Converting movies
- Multi-frame rendering
- Automated rendering and network rendering
- Rendering and exporting withal images and still-image sequences
- Using the GoPro CineForm codec in Later Effects
- Working with other applications
- Dynamic Link and Afterward Effects
- Working with After Effects and other applications
- Sync Settings in Later on Effects
- Artistic Cloud Libraries in Later Effects
- Plug-ins
- CINEMA 4D and Cineware
- Collaboration: Frame.io, and Team Projects
- Collaboration in Premiere Pro and After Furnishings
- Frame.io
- Install and activate Frame.io
- Use Frame.io with Premiere Pro and After Furnishings
- Often asked questions
- Team Projects
- Get Started with Squad Projects
- Create a Team Project
- Collaborate with Team Projects
- Memory, storage, performance
- Memory and storage
- Improve operation
- Preferences
- GPU and GPU commuter requirements for Subsequently Effects
Move tracking overview and resources
With movement tracking, you can track the movement of an object and so utilize the tracking data for that move to another object—such as another layer or an effect control point—to create compositions in which images and effects follow the motion. Y'all tin also stabilize motion, in which case the tracking data is used to animate the tracked layer to recoup for move of an object in that layer. You lot can link properties to tracking data using expressions, which opens up a wide diverseness of uses.
After Effects tracks motion by matching image data from a selected area in a frame to prototype data in each succeeding frame. You tin apply the aforementioned tracking data to different layers or effects. Yous can as well track multiple objects in the same layer.
In After Effects, you can track camera motility and place 3D objects in 2nd footage much more easily using the 3D camera tracker. For more information, see Tracking 3D camera movement.
Uses for motion tracking and stabilization
Movement tracking has many uses. Hither are some examples:
-
Combining elements filmed separately, such as calculation video to the side of a moving metropolis bus or a star to the stop of a sweeping wand.
-
Animating a still image to match the motion of activity footage, such every bit making a drawing bumblebee sit on a swaying bloom.
-
Animative furnishings to follow a moving element, such equally making a moving ball glow.
-
Linking the position of a tracked object to other properties, such every bit making stereo sound pan from left to correct as a car races across the screen.
-
Stabilizing footage to agree a moving object stationary in the frame to examine how a moving object changes over time, which can be useful in scientific imaging piece of work.
-
Stabilizing footage to remove the jostling (photographic camera shake) of a handheld photographic camera.
Depending on the encoder yous use, it is possible to subtract the size of your last output file by stabilizing motility footage. Random motion, such as from the jostling of a handheld camera, can make it hard for many compression algorithms to compress your video.
Motion tracking user interface and terminology overview
Y'all set upwards, initiate, and apply motion tracking with the Tracker panel.
Equally with all properties, yous tin modify, animate, manage, and link tracking properties in the Timeline panel.
You specify areas to runway by setting track points in the Layer console. Each track point contains a feature region, a search region, and an adhere point. A gear up of rails points is a tracker.
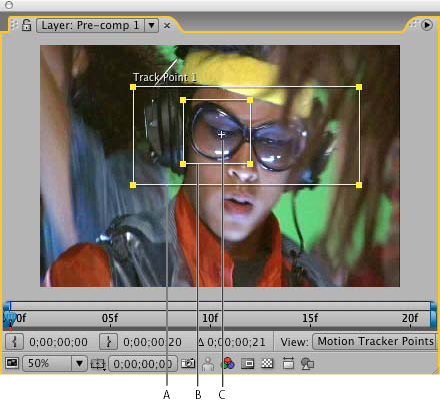
A. Search regionB. Feature regionC. Adhere point
Feature region
The feature region defines the element in the layer to be tracked. The feature region should surround a distinct visual element, preferably one object in the real earth. After Furnishings must exist able to clearly identify the tracked feature throughout the elapsing of the track, despite changes in light, groundwork, and angle.
Search region
The search region defines the area that After Effects will search to locate the tracked characteristic. The tracked feature needs to exist distinct simply within the search region, not within the entire frame. Confining the search to a minor search region saves search time and makes the search process easier, just runs the risk of the tracked feature leaving the search region entirely betwixt frames.
Adhere point
The adhere indicate designates the identify of zipper for the target —the layer or outcome control betoken to synchronize with the moving characteristic in the tracked layer.
When you begin tracking, After Furnishings sets the quality of the motion source layer to Best and the resolution to Total in the Composition and Layer panels, which makes the tracked feature easier to find and enables subpixel processing and positioning.
Subsequently Effects uses one runway point to track position, ii track points to track scale and rotation, and four points to perform tracking using corner pinning.
Online resources for movement tracking and stabilization
- Mocha Essentials is a gratuitous video training series from Boris FX that teaches everything you need to know well-nigh Mocha AE and Planar Motion Tracking.
- Curtis Sponsler provides detailed instructions and explanations for tracking and stabilizing motion in a PDF excerpt from his volume The Focal Easy Guide to After Furnishings.
- Chris and Trish Meyer provide a video tutorial on the ProVideo Coalition website that demonstrates and explains the basics of motility tracking.
- Angie Taylor provides a tutorial on the Digital Arts website that shows how to utilize tracking data and the Clone Stamp tool to apply copies of an object in a scene while matching a camera move.
- This post on the AE Enhancers forum describes and links to an blitheness preset from Donat van Bellinghen for scaling a set of Corner Pivot upshot points.
- This mail on the AE Enhancers forum describes and links to a script from Paul Tuersley that takes a stabilized layer, precomposes information technology, and and so adds expressions that counter the stabilization.
- Jörgen Persson provides a script on the After Effects Scripts website with which yous tin import tracking data from Apple tree Shake into After Effects.
Planar Tracking with Mocha AE
After Effects includes the Mocha AE plug-in from Boris FX, which is GPU-accelerated, and Multi-Frame Rendering supported. Apply the plug-in to piece of work with complex tracking shots such as shots with motion blur or objects that move off-screen.It displays in the Essentials workspace by default and contains the bones functionalities. To use the avant-garde features, such as AdjustTrack, select Workspace > Classic afterward you launch Mocha AE.
To apply Mocha AE a Mocha spline as an alpha-based matte: After applying the Mocha AE result, in the Effects Control panel nether Matte, select Utilize Matte. This option supports Mocha'south edge feathering.
To convert a Mocha AE layer to a native After Effects mask: After applying the Mocha AE effect, in the Effects Control panel nether Matte, select Create AE Masks. This choice ignores Mocha'due south edge feathering.
To use Mocha AE:
- Select a footage layer in your composition and select Effect > Boris FX Mocha > Mocha AE .
- Click the Mocha logo in the Consequence Controls panel to launch the user interface.
OR
Utilize Mocha AE after you select a layer in your composition past selectingBlitheness > Runway in Boris FX Mocha.
Applying Mocha AE data in After Effects
You tin can use the Mocha AE data within After Effects in multiple means:
- Replace screens with perspective using corner pivot blitheness.
- Transformation blitheness (position, scale & rotation) for general motility tracking.
- To Rotoscope, catechumen Mocha AE tracked splines to Afterwards Effects masks.
Later you complete tracking in Mocha AE, exit dorsum to Afterward Effects and use the post-obit steps:
- In the Effects Control panel under Tracking Data , select Create Track Data . Then select either Corner Pivot or Transform.
- Apply Export to the selected layer.
To convert a Mocha AE layer to a native After Furnishings mask, in the Furnishings Control panel under Matte, select Create AE Masks.
To acquire more about Mocha AE, refer to the following resources:
- Mocha Essentials video serial
- Mocha user guide
The Mocha AE plug-in tin convert spline shapes from Mocha AE to either rasterized mattes for After Effects layers or to native After Furnishings masks. For more information, run across Resource for Mocha AE Masking.
Motion tracking workflows
There are many ways you tin can do motion tracking in After Furnishings, and the method and workflow you follow depend on the nature of your prune, and what you want to runway.
Mask tracker
Apply the mask tracker to draw masks around your object to rails only certain objects in your scene.
For detailed information on the mask tracker, see Mask Tracking.
Face tracker
Simple mask tracking lets you quickly apply furnishings only to a confront, such as selective color correction or blurring a person's face, and more.
However, with Face Tracking, you tin can runway specific parts of the confront such as pupils, oral cavity, and nose, allowing you to isolate and piece of work on these facial features with greater detail. For case, change colors of the eyes or exaggerate mouth movements without frame-by-frame adjustments.
For detailed instructions on using the face tracker, see Face Tracking.
3D Camera tracker
Utilise the 3D camera tracker issue to analyze video sequences to extract photographic camera motion and 3D scene data. You lot tin can then correctly composite 3D elements over your 2D footage.
For detailed instructions on using the 3D camera tracker, run across Tracking 3D camera movement.
Indicate tracker
You tin track one or multiple reference features in a clip:
-
Ane-point tracking: Track a single reference pattern (a modest area of pixels) in a moving-picture show clip to record position data.
-
Two-point tracking: Track two reference patterns in a moving-picture show clip and apply the human relationship between the two tracked points to record position, calibration, and rotation data.
-
Four-bespeak tracking or Corner pivot runway: Track iv reference patterns in a flick clip to record position, scale, and rotation data. The four trackers analyze the human relationship betwixt four reference patterns, such as the corners of a movie frame or tv monitor. This data is applied to each corner of an prototype or clip to "pivot" the clip and then that information technology appears locked in the picture frame or idiot box monitor.
- Multiple-point tracking: Track every bit many reference patterns in a clip every bit y'all like. You can manually add together trackers within the Analyze Motility and Stabilize behaviors. When you apply a Track Points behavior from the Shape behaviors subcategory to a shape or mask, a tracker is automatically assigned to each shape control bespeak.
For detailed instructions on using the point tracker, meet Tips for using the point tracker.
Warp stabilizer VFX
You tin can stabilize movement with the Warp Stabilizer effect. It removes jitter caused by camera movement, making it possible to transform shaky, handheld footage into steady, shine shots.
For more than information, meet Stabilize motility with the Warp Stabilizer VFX effect.
See Tracking and stabilizing motion for more information about using the point tracker for stabilizing move.
For video tutorials, details, and resource about the Warp Stabilizer issue, come across this article on the Adobe website.
Tips for using the bespeak tracker
For motility tracking to get smoothly, you must have a proficient feature to track, preferably a distinctive object or region.
For best results, gear up the object or region that you are tracking before yous brainstorm shooting. Because After Furnishings compares image information from one frame to the next to produce an authentic track, attaching high-contrast markers to the object or region lets After Effects more easily follow the motion from frame to frame. Lightweight, brightly colored balls (such as ping-pong balls) placed on the feature work well, in part because their appearance is the same from all angles. The number of markers that you use corresponds to the number of points you are tracking. For example, if you're tracking four points using the Perspective Corner Pinning choice, you'll track four features, to correspond to the four corners of the layer to attach. The more markers you add to your subject before shooting, the more features y'all'll accept for tracking—merely the more items you may have to remove later on from the image with the Clone Postage tool. You lot don't need to add together a marker for each characteristic if a distinctive object or region is already at the advisable location.
If you're tracking a large object or the set up itself—such as for lucifer-moving—you can get good results by using a grid of uniformly spaced triangles of a uniform size as tracking markers.
Add the appropriate number of track points
When you lot choose a fashion from the Rails Blazon menu in the Tracker panel, Subsequently Effects places the appropriate number of track points in the Layer panel for that mode. Y'all can add more track points to track boosted features with one tracker.
Select features to track, and place characteristic regions
Earlier you begin tracking, view the entire duration of the shot to decide the best features to rail. What is clearly identifiable in the first frame may afterward blend into the background considering the angle, lighting, or surrounding elements have inverse. A tracked feature may disappear off the edge of the frame or be obscured by another chemical element at some point in the scene. Though After Effects can extrapolate the motion of a feature, your chances for successful tracking are highest if you step through the entire shot to select the best candidates for tracking.
A practiced tracked feature has these characteristics:
-
Visibility for the unabridged shot
-
A contrasting color from the surrounding area in the search region
-
A singled-out shape inside the search region
-
A consistent shape and colour throughout the shot
Set the attach point showtime
The adhere point is where the target layer or effect control point will be placed. The default attach betoken position is in the heart of the feature region. Yous can move the attach point to offset the position of the target relative to the position of the tracked feature by dragging the attach point in the Layer console earlier tracking.
For example, to animate a cloud to a higher place a person'south caput, position the feature region on the head and move the attach point above the head. If yous left the attach indicate centered in the feature region, the cloud would be attached to that betoken and would obscure the caput.


Adjust the feature region, search region, and tracking options
Identify each feature region control tightly around its tracked feature, completely enclosing the tracked feature, but including as little of the surrounding image as possible.
The size and position of the search region depend on the movement of the feature yous want to runway. The search region must accommodate the movement of the tracked feature, but just the frame-to-frame movement, non its motion throughout the shot. As After Effects locates the tracked feature in a frame, both the feature region and search region move to the new location. Therefore, if the frame-to-frame movement of the tracked characteristic is gradual, and then the search region needs to be only slightly larger than the characteristic region. If the feature changes position and direction rapidly, then the search region needs to be big enough to encompass the largest position and direction alter in whatsoever pair of frames.
You can also fix tracking options that determine such things as which color channels are compared to find a match to the feature region.
Y'all perform the bodily motion tracking pace by clicking 1 of the Clarify buttons in the Tracker console. When tracking a tricky set of features, yous may want to analyze a frame at a time.
Because of the irresolute nature of an image in motion, automatic tracking is rarely perfect. In moving footage, the shape of a characteristic changes, forth with the lighting and surrounding objects. Even with careful preparation, a feature generally changes during a shot and at some point no longer matches the original characteristic. If the change is too great, Afterwards Furnishings may non be able to track the feature, and the runway bespeak volition wander or drift.
When the analysis begins to fail, return to the frame where tracking was still authentic and echo the adjust and analyze steps.
If you're using any Rail Type setting other than Raw, yous employ tracking data by clicking Apply, after making sure that the right target is shown for Move Target. You apply tracking data from a Raw tracking operation by copying keyframes from the trackers to other properties or by linking properties with expressions.
You can also conform the Attach Point or Attach Point Commencement belongings later on tracking in the Timeline console, which tin be useful when applying the aforementioned tracking information to multiple targets that you want to distribute around the tracked feature.
If the layer that yous're attaching has motion blur enabled, make certain that the Shutter Stage value is set to -i/2 times the Shutter Angle value. This combination of settings centers the motion blur on the attach betoken. Otherwise, the attached object may appear to atomic number 82 or lag the object that information technology'southward attached to.
You can utilize the tracking data to a zippo object layer and parent the layer that yous want to animate to the null object layer.
Rail or stabilize movement with the indicate tracker
Tracking motion and stabilizing motion are essentially the same process, merely with a different target and issue. Use Rail Motion to rail move and apply the results to a different layer or upshot control indicate. Utilize Stabilize Motion to rail motion and apply the results to the tracked layer to compensate for that move (for example, to remove camera milk shake).
To stabilize a layer, Subsequently Effects tracks the movement of a feature in the layer that should be stationary in the frame, and then uses the tracking information to set keyframes to perform the reverse motion. Y'all can stabilize to remove whatsoever combination of changes in position, rotation, and scale, while leaving desired motion unaffected. For case, if the camera is panning, deselect Position simply select Scale and Rotation as the properties to stabilize.
When you select Rotation or Calibration in the Tracker panel, you set two track points in the Layer panel. A line connects the attach points; an arrow points from the get-go attach betoken (the base of operations) to the second. If possible, identify the feature regions on opposite sides of the same object, or at least on objects that are the same distance from the photographic camera. The farther apart the regions, the more accurate the calculations and the amend the result.
Later on Effects calculates rotation by measuring the alter of bending of the line between the adhere points. When you lot apply the tracking data to the target, After Effects creates keyframes for the Rotation holding.
Afterwards Effects calculates scale by comparing the distance betwixt attach points on each frame with the distance between the attach points on the start frame. When you apply the tracking information to the target, Later Effects creates keyframes for the Scale belongings.
When you lot runway motion using either parallel or perspective corner-pinning, After Effects applies keyframes for the Corner Pivot result to the layer to scale and skew the target layer as necessary to fit the four-sided area defined by the feature regions. The feature regions should lie in a single plane in the real world—for example, on the side of a bus, on the same wall, or on the floor. The attach points should also all lie in a unmarried aeroplane, but not necessarily the aforementioned plane as the characteristic regions.
For parallel corner-pinning merely: To alter which indicate is inactive, Alt-click (Windows) or Option-click (Mac Os) the feature region of the betoken to make inactive. (One point must remain inactive to keep the lines parallel.)
-
Select the layer to track in the Timeline panel.
-
- Click Track Motion in the Tracker panel (or choose Blitheness > Track Motion), click Edit Target, and choose the target to apply the tracking information to.
- Click Stabilize Motion in the Tracker panel (or choose Blitheness > Stabilize Movement). The target layer is the tracked (source) layer.
-
Select Position, Rotation, and/or Calibration to specify what kinds of keyframes to generate for the target.
-
Move the current-time indicator to the frame from which to begin tracking.
-
Using the Selection tool, adjust the feature region, search region, and attach point for each track bespeak.
-
In the Tracker panel, click either the Analyze Forward or Analyze Backward button to begin tracking.
If the tracking ceases to be accurate, click the Terminate push button
 , correct the trouble as described in Right a motion rail, and resume analysis.
, correct the trouble as described in Right a motion rail, and resume analysis. -
When you are satisfied with the position of the feature region and attach indicate throughout the rail, click the Utilise push to utilise the motion to the specified target.
After Effects creates keyframes for the target layer.
When tracking position and applying this position information to a target, you lot can choose to utilize simply the x (horizontal) or y (vertical) component of movement. For instance, you lot tin apply the tracking data to the x axis to make a speech bubble (the motion target) remain at the top of the frame even when the player (the motility source) moves downward.
-
Ten And Y (default) allows motion along both axes.
-
10 Only restricts the motility target to horizontal movement.
-
Y Only restricts the motion target to vertical motion.
To bypass the Motion Tracker Apply Options dialog box and use the previous setting, hold Alt (Windows) or Choice (Mac Os) as yous click Utilise.
-
Y'all can change the order of steps 1-three by first selecting the property to which to apply the tracking data (Scale, Position, or Rotation) and then choosing Animation > Runway This Belongings. After Effects prompts y'all to choose the layer to use as a motion source.
When y'all stabilize a layer, the compensating move may itself cause the layer to motion too far in one direction, exposing the groundwork in the composition or moving action out of the action-prophylactic zone. You lot can correct this with a small modify in scale for the layer. Discover the frame where the trouble is virtually severe, and so increase or decrease the calibration of the layer until the problem is resolved. This technique adjusts the calibration for the elapsing of the layer; y'all tin also breathing calibration to right this problem by zooming in and out at different times.
Motion tracking controls
Yous set up, initiate, and apply motion tracking with the Tracker console.
Move Source
The layer that contains the motion to runway.
Layers are available in the Move Source bill of fare if they have source footage items that tin contain motion or if they are composition layers. You tin precompose a layer to brand information technology available in the Motion Source menu.
Current Runway
The active tracker. You lot tin modify settings for a tracker at any time by selecting the tracker from this bill of fare.
Rail Type
The tracking mode to use. The motion tracking itself is the same for each of these modes; they differ in the number of track points and how the tracking data is practical to the target:
-
Stabilize tracks position, rotation, and/or scale to compensate for movement in the tracked (source) layer. When tracking position, this way creates one track point and generates Anchor Indicate keyframes for the source layer. When tracking rotation, this mode creates two rails points and produces Rotation keyframes for the source layer. When tracking scale, this mode creates two rail points and produces Calibration keyframes for the source layer.
-
Transform tracks position, rotation, and/or calibration to utilise to some other layer. When tracking position, this fashion creates one track bespeak on the tracked layer and sets Position keyframes for the target. When tracking rotation, this mode creates two rails points on the tracked layer and sets Rotation keyframes for the target. When tracking scale, this manner creates two track points and produces Scale keyframes for the target.
-
Parallel Corner Pin tracks skew and rotation, but not perspective; parallel lines remain parallel, and relative distances are preserved. This way uses three rail points in the Layer console—and calculates the position of the fourth—and sets keyframes for 4 corner points in a Corner Pin upshot belongings grouping, which is added to the target. The four attach points mark the placement of the four corner points.
-
Perspective Corner Pivot tracks skew, rotation, and perspective changes in the tracked layer. This manner uses four track points in the Layer panel and sets keyframes for four corner points in a Corner Pin outcome property group, which is added to the target. The iv attach points mark the placement of the four corner points. This selection is useful for attaching an image to an opening door or the side of a motorbus that'due south turning a corner.
-
Raw tracks position just. Use Raw to generate tracking data that y'all won't use using the Apply button. For case, you can re-create and paste the keyframes for the Attach Point property to the Position property for a paint stroke; or, you tin link effect properties for the Stereo Mixer effect to the ten coordinate of the Attach Point belongings using expressions. Tracking data is stored on the tracked layer. The Edit Target push and the Apply button are non available with this tracking option. You tin add together track points to a tracker by choosing New Track Point from the Tracker panel menu.
Movement Target
The layer or effect control point that the tracking data is applied to. Afterwards Effects adds properties and keyframes to the target to motility or stabilize it. Change the target by clicking Edit Target. No target is associated with a tracker if Raw is selected for Track Blazon.
Clarify buttons
Begins the frame-to-frame analysis of the rail point in the source footage:
-
Analyze one Frame Backward
 : Analyze the electric current frame by moving back to the previous frame.
: Analyze the electric current frame by moving back to the previous frame. -
Clarify Backward
 : Clarify from the current-time indicator astern to the beginning of the trimmed layer duration.
: Clarify from the current-time indicator astern to the beginning of the trimmed layer duration. -
Analyze Forward
 : Analyze from the current-time indicator to the terminate of the trimmed layer elapsing.
: Analyze from the current-time indicator to the terminate of the trimmed layer elapsing. -
Analyze i Frame Forward
 : Analyze the current frame by advancing to the next frame.
: Analyze the current frame by advancing to the next frame.
While analysis is in progress, the Clarify Backward and Analyze Forward buttons change to a Stop push, with which y'all tin can stop assay when the runway drifts or otherwise fails.
Reset
Restores the feature region, search region, and attach point to their default positions and deletes the tracking data from the currently selected track. Tracker control settings and keyframes already applied to the target layer remain unchanged.
Use
Sends the tracking data (in the form of keyframes) to the target layer or effect control signal.
Motility tracking options
These settings apply to a tracker, a group of track points that is generated in one tracking session. You can modify these settings by clicking Options in the Tracker panel.
Track Name
The name for a tracker. You can also rename a tracker by selecting information technology in the Timeline panel and pressing Enter on the chief keyboard (Windows) or Return (Mac Bone).
Tracker Plug-in
The plug-in used to perform move tracking for this tracker. By default, this option displays Congenital-in, the only tracking plug-in included with Later on Effects.
Channel
The components of the image data to use for comparison when searching for a match for the feature region. Select RGB if the tracked feature is a distinct color. Select Luminance if the tracked feature has a unlike brightness than the surrounding image (such equally a burning candle carried through a room). Select Saturation if the tracked feature has a loftier concentration of color, surrounded past variations of the aforementioned color (such as a bright scarlet scarf against a brick wall).
Process Earlier Lucifer
Temporarily blurs or sharpens an paradigm to better tracking. Mistiness reduces racket in the footage. Usually a value of 2 to 3 pixels is enough to produce better tracks in grainy or noisy footage. Heighten exaggerates or refines the edges of an image and makes them easier to rails.
After Effects blurs or enhances the layer merely for tracking. This blurring does non bear upon the motion source layer.
Track Fields
Temporarily doubles the frame rate of the limerick and interpolates each field to a full frame to track motion in both fields of interlaced video.
Subpixel Positioning
When selected, keyframes are generated to a precision of a fraction of a pixel. When deselected, the tracker rounds off values to the nearest pixel for generated keyframes.
Adapt Feature On Every Frame
Causes Later on Effects to arrange the tracked feature for each frame. The image data that is searched for within the search region is the paradigm information that was within the feature region in the previous frame, rather than the image information that was in the feature region at the beginning of analysis.
If Confidence Is Below
Specifies the action to perform when the Confidence holding value is beneath the pct value that you specify.
To determine an adequate conviction threshold, track the move and then examine the Confidence values for the track bespeak in the Timeline panel for problematic frames. Specify a confidence value that is slightly larger than the largest confidence value for the problematic frames.
- Select Continue Tracking to ignore the Confidence value. This behavior is the default behavior.
- Select Terminate Tracking to terminate the motion tracking.
- Select Extrapolate Movement to estimate the position of the feature region. Attach-bespeak keyframes aren't created for depression-confidence frames, and attach-signal keyframes for the low-confidence frames from previous tracks are deleted.
- Select Adapt Characteristic to utilize the original tracked feature until the confidence level falls beneath the specified threshold. At that point, After Effects adapts the tracked feature to be the contents of the feature region in the frame preceding the one that has low confidence and continues tracking. This pick isn't available if Arrange Feature On Every Frame is selected in the Motion Tracker Options dialog box; enabling feature adaptiveness causes After Effects to arrange the characteristic region with every frame regardless of the conviction level.
Options
Opens the Tracker Plug-in Options dialog box, which includes options for the AE Original Built-in Tracker. This command is available but if you lot choose to use the older Later on Effects tracker plug-in.
To prove or hide motion paths in the Layer panel, select or deselect the Display Motion Paths pick in the panel carte du jour of the Tracker console. (The panel menu is the bill of fare that you lot admission by clicking the icon in the upper-right corner of a panel.) You can as well utilize commands in this carte to add a new track indicate, reveal the current track in the Timeline panel, and toggle whether the feature region magnification is enabled.
Movement tracking backdrop in the Timeline panel
Each fourth dimension you click Runway Motion or Stabilize Motion in the Tracker console (or cull Animation > Track Motion or Blitheness > Stabilize Motility), After Effects creates a new tracker for the layer in the Timeline panel. Each tracker contains track points, which are holding groups that shop the tracking data after tracking has been performed. After Furnishings groups trackers in the Motion Trackers holding grouping for each layer in the Timeline panel.
To show a tracker in the Timeline panel, select the tracker from the Current Rails menu in the Tracker panel and press SS.
Y'all can rename trackers and track points and modify and breathing their holding values in the Timeline panel simply equally you lot do for other layer properties and property groups. Yous must click Employ in the Tracker panel to apply the property changes to the target.
Feature Middle
Position of the middle of the feature region.
Feature Size
Width and summit of the feature region.
Search Offset
Position of the heart of the search region relative to the center of the feature region.
Search Size
Width and height of the search region.
Confidence
Property through which After Furnishings reports the amount of certainty regarding the match made for each frame. In general, Confidence is not a holding that you modify.
Attach Point
Position assigned to the target layer or effect control point.
Attach Point Offset
Position of the attach indicate relative to the center of the feature region.
Adapt the track point
When you gear up upwardly motion tracking, information technology's often necessary to refine your runway point by adjusting the feature region, search region, and adhere indicate. Y'all can resize or move these items independently or in groups by dragging using the Selection tool. To help you define the area to be tracked, the paradigm expanse within the characteristic region is magnified to 400% while you move the region.
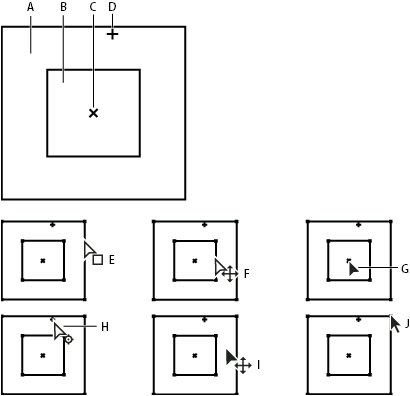
A. Search regionB. Characteristic regionC. Keyframe markerD. Attach pointE. Moves search regionF. Moves both regionsG. Moves entire rail indicateH. Moves attach bespeakI. Moves entire rail signalJ. Resizes region
- To plow on or off feature region magnification, choose Magnify Feature When Dragging from the Tracker panel menu.
- To move the feature region, search region, and attach point together, drag inside the track point expanse (avoiding the region edges and the adhere signal), or press the Up, Downwardly, Left, or Correct Pointer fundamental. Hold Shift while pressing an pointer fundamental to movement by an increment 10 times as big.
- To move only the feature and search regions together, drag the edge of the feature region, or Alt-elevate (Windows) or Option-drag (Mac OS) with the Selection tool inside the feature or search region. Y'all tin can also hold Alt (Windows) or Option (Mac Os) while pressing the Upward, Downwards, Left, or Right Arrow key. Concord Alt+Shift (Windows) or Option+Shift (Mac Bone) while pressing an pointer primal to motility past an increment x times as large.
- To movement simply the search region, drag the edge of the search region.
Kickoff the search region eye from the feature region center in the direction in which the tracked feature is traveling.
- To move only the attach signal, elevate the attach point.
- To resize the feature or search region, drag a corner handle.
- To make all of the sides of the region friction match the length of the longest side, and to resize the region relative to the original eye point of the region, Shift-drag a corner handle.
- To make all of the sides of the region friction match the length of the longest side, and to resize the region relative to a particular corner handle, Ctrl+Shift-drag (Windows) or Command+Shift-drag (Mac Bone) the opposite corner handle.
To restrict the movement of the track betoken to the x (horizontal) or y (vertical) axis during tracking, resize the pinnacle or width of the search region to match the height or width of the feature region.
Apply tracking data to a new target
After you've tracked a move source layer, you can employ the tracking information stored on that layer to whatsoever number of other target layers and event command points. For instance, you can apply the track to the position of a light bulb and to the effect control point of the Lens Flare effect.
-
In the Tracker console, cull the tracked layer from the Motion Source menu.
-
Choose the track that contains the tracking information you want from the Electric current Rails bill of fare.
-
Click Edit Target, and choose the target.
-
In the Tracker panel, click the Apply button.
Correct a motion track
Every bit an image moves in a shot, the lighting, surrounding objects, and angle of the object can all change, making the one time-distinct feature no longer identifiable at the subpixel level. Too, if the search region is likewise small, the tracked feature may leave its premises from ane frame to the side by side.
Learning to choose a trackable feature takes time. Even with conscientious planning and practice, the feature region can migrate away from the desired feature. Re-adjusting the feature and search regions, changing the tracking settings, and trying again is a standard role of automatic tracking. It's not necessary to get a single expert track in 1 effort. Y'all may demand to track the shot in sections, redefining the feature region in places where the characteristic changes and the region drifts. You may fifty-fifty demand to choose a different feature to track, one with movement that closely matches that of the feature to rails, and use the adhere bespeak offset to place the target.
After you've tracked motion, each runway point has a motility path in the Layer panel that shows the position of the middle of the characteristic region. Y'all can fine-tune the keyframes of the motion path in the Layer panel every bit you would whatsoever other motility path. Modifying the movement path is most useful when y'all want to manually change the move tracking data before applying information technology to a target. In some cases, it may be easier to manually modify the motion path created by the motion tracker than to go a perfect track.
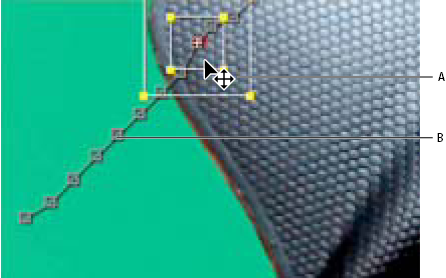
A. Moving the feature and search regionsB. Keyframe marking
Correct drifting by adjusting the feature and search regions
-
Move the current-time indicator to the last well-tracked frame.
-
Alt-drag (Windows) or Option-elevate (Mac Bone) the feature and search regions but (not the attach signal) to the correct location.
-
If you lot are correcting the track for ane frame, become to pace 4. If you are correcting the rails for several contiguous frames, conform the feature region and search region if necessary, and click Analyze. Watch the tracking to make sure that it is accurate. If the tracking is not accurate, and then click the push button again to stop tracking, conform the feature region, and begin again.
-
When you lot are satisfied with the rail, click Utilize to apply the keyframes to the target layer or effect control point.
Correct drifting by modifying tracking settings
-
Move the current-time indicator to the last well-tracked frame.
-
In the Tracker panel, click Options.
-
In the Tracker console, click the Clarify Forward or the Analyze Backward push button.
-
Watch the tracking to make sure that information technology is accurate. If the tracking is not authentic, then click the push button again to stop tracking, adjust the settings, and begin again.
-
When you are satisfied with the rails, click Employ to apply the keyframes to the target layer or effect control point.
Stabilize motion with the Warp Stabilizer VFX effect
You lot can stabilize motion with the Warp Stabilizer issue. Information technology removes jitter caused by camera movement, making it possible to transform shaky, handheld footage into steady, smooth shots. Run across Tracking and stabilizing move for more than information about using the bespeak tracker for stabilizing motion.
For video tutorials, details, and resources virtually the Warp Stabilizer result, see this article on the Adobe website.
Warp Stabilizer VFX | After Effects CC
An upgrade to the Warp Stabilizer, VFX adds the ability to choose which objects within a scene get stabilized.
Stabilize with the Warp Stabilizer effect
To stabilize move using the Warp Stabilizer effect, do the post-obit:
-
Select the layer you desire to stabilize.
-
In Afterwards Furnishings CC:
- Go to the Effects & Presets panel > Distort and use the Warp Stabilizer VFX to the layer.
- Right-click the footage item in the Timeline panel and choose Warp Stabilizer VFX.
After the effect is added to the layer, analysis of the footage begins immediately in the groundwork. As analysis begins, the first of two banners displays in the Composition panel indicating that analysis is occurring. When analysis is consummate, the 2d imprint displays a message that stabilization is occurring.
Yous are gratis to work with the footage or elsewhere in the project while these steps are occurring.
Warp Stabilizer VFX / settings
In that location is no need to press this push button when y'all beginning use Warp Stabilizer; it'south pressed for you automatically. The Analyze push button remains dimmed until some change takes place. For example, if you lot suit a layer's In or Out points, or at that place is an upstream alter to the layer source. Click the button to reanalyze the footage.
Assay does not take into account any masks or effects that are applied direct to the aforementioned layer. Pre-compose and place them in the upstream limerick if you lot desire them to be analyzed.
Cancels an analysis in progress. During analysis, status information appears next to the Cancel button.
Stabilization settings let for adjusting the stabilization process.
Result
Controls the intended event for the footage (Polish or No Motility).
-
Smoothen movement (default): Retains the original camera motion but makes it smoother. When selected, Smoothness is enabled to command how smooth the photographic camera motility becomes.
-
No Movement: Attempts to remove all camera move from the shot. When selected, the Crop Less <-> Smooth More function is disabled in the Avant-garde section. This setting is used for footage where at least a portion of the main subject remains inside the frame for the entire range being analyzed.
Smoothness
Chooses how much the camera's original motion is stabilized. Lower values are closer to the camera'southward original movement while higher values are smoother. Values above 100 require more than cropping of the image. Enabled when the Result is set to Smooth Motility.
Method
Specifies the most complex functioning the Warp Stabilizer performs on the footage to stabilize information technology:
-
Position Tracking is based on position data only and is the nigh bones way footage can be stabilized.
-
Position, Scale And Rotation Stabilization is based upon position, calibration, and rotation information. If there are not plenty areas to track, Warp Stabilizer chooses the previous type (Position).
-
Perspective: Uses a blazon of stabilization in which the entire frame is effectively corner-pinned. If at that place are not plenty areas to runway, Warp Stabilizer chooses the previous blazon (Position, Scale, Rotation).
-
Subspace Warp (default): Attempts to warp various parts of the frame differently to stabilize the entire frame. If there are not enough areas to rails, Warp Stabilizer cull the previous type (Perspective).
The method in use on any given frame can alter across the course of the clip based on the tracking accuracy.
Notation: In some cases, Subspace Warp can introduce unwanted warping, and Perspective can innovate unwanted keystoning. You can forbid anomalies by choosing a simpler method.
Preserve Scale
(After Effects) When enabled, prevents the Warp Stabilizer from trying to adjust forward and astern camera movements with scale adjustments.
Borders
Borders settings adjust how borders (the moving edges) are treated for footage that is stabilized.
Framing
Controls how the edges appear in a stabilizing result. Framing can exist set to one of the following:
- Stabilize Only: Displays the entire frame, including the moving edges. Stabilize Only shows how much work is being washed to stabilize the prototype. Using Stabilize Only allows you to crop the footage using other methods. When selected, the Auto-calibration section and Crop Less <-> Smooth More than property are disabled.
- Stabilize, Ingather: Crops the moving edges without scaling. Stabilize, Crop is identical to using Stabilize, Crop, Auto-scale, and setting Maximum Scale to 100%. With this option enabled, the Car-scale section is disabled, merely the Crop Less <-> Smooth More holding is enabled.
- Stabilize, Crop, Auto-scale (default): Crops the moving edges and scales up the image to refill the frame. The automatic scaling is controlled by various backdrop in the Auto-scale department.
- Stabilize, Synthesize Edges: Fills in the blank space created past the moving edges with content from frames earlier and after in time (controlled by Synthesizes Input Range in the Advanced section). With this option, the Auto-scale section and Crop Less <-> Smooth More are disabled.
It is possible for artifacts to announced when at that place is motility at the edge of the frame non related to camera movement.
Machine-scale
Displays the current auto-scale amount, and allows you to set limits on the amount of auto-scaling. Enable Auto-scale by setting framing to Stabilize, Crop, Motorcar-scale.
- Maximum Calibration: Limits the maximum amount a clip is scaled upward for stabilization.
- Action-Safe Margin: When non-naught, specifies a border effectually the edge of the image that you don't expect to be visible. Thus, auto-calibration does not try to fill it.
Additional Scale
Scales up the prune with the same consequence every bit scaling using the Scale property under Transform, but avoids an extra resampling of the paradigm.
Detailed Analysis
When set to on, makes the adjacent Analysis stage exercise extra work to find elements to track. The resulting data (stored in the project as role of the effect) is much larger and slower with this choice enabled.
Rolling Shutter Ripple
The stabilizer automatically removes the rippling associated with stabilized rolling shutter footage. Automatic Reduction is the default. Employ Enhanced Reduction if the footage contains larger ripples. To employ either method, prepare the Method to Subspace Warp or Perspective.
Ingather Less <-> Smoothen More
When cropping, controls the merchandise-off between smoothness and scaling of the cropping rectangle as it moves over the stabilized image. Lower values are smooth, notwithstanding, more than of the image is viewed. At 100%, the result is the aforementioned as the Stabilize Only option with manual cropping.
Synthesis Input Range (seconds)
Used past Stabilize, Synthesize Edges framing, controls how far backward and forward in time the synthesis process goes to fill in any missing pixels.
Synthesis Edge Plumage
Selects the corporeality of feather for the synthesized pieces. It is enabled only when using the Stabilize, Synthesize Edges framing. Use the feather control to smooth over edges where the synthesized pixels join up with the original frame.
Synthesis Edge Cropping
Trims off the edges of each frame before it is used to combine with other frames when using the Stabilize, Synthesize Edges framing option. Use the cropping controls to crop off bad edges that are mutual in analog video capture, or low quality optics. Past default, all edges are fix to zero pixels.
Objective
Determines the aim for the event: for stabilizing, for temporary stabilization to perform visual effects work, or to composite a layer into a shaky scene. Choose an objective:
- Stabilize Default option for normal stabilization
- Reversible Stabilization and Reverse Stabilization Employ these options to apply an effect to a region. Use ii instances of the Warp Stabilizer VFX effect, one with Reversible Stabilization to steady a shaky object, and a duplicate case with Reverse Stabilization to insert the shake back in, so that whatsoever effects you apply after Reversible Stabilization appear within the original scene.
- Use Motion to Target and Utilise Motion to Target over Original Use these options to composite a layer into a shaky scene to employ the stabilized motion onto a different layer.
Target Layer
Cull a layer to which the stabilized motion is applied using the Apply Motion to Target or Apply Motion to Target over Original options.
Show Rail Points
Determines if track points are displayed.
Runway Point Size
Determines the size of the displayed track points
Machine-delete Points Beyond Fourth dimension
When y'all delete track points in a composition panel, corresponding track points on the same object, are deleted at other times on the layer. You do non need to manually delete the track points frame-by-frame.
Hide Warning Banner
Apply when you lot don't want to reanalyze footage even though at that place is a alert banner indicating that information technology must be reanalyzed.
Warp Stabilizer workflow tips
-
Employ Warp Stabilizer VFX.
-
While the Warp Stabilizer result is analyzing your footage, yous can conform settings or piece of work on a different part of your projection.
-
Cull Stabilization > Result > No Motion if you want to completely remove all photographic camera motion. Choose Stabilization > Result > Smooth Motion if you want to include some of the original camera motion in the shot.
-
If the result is practiced, y'all're done with stabilization. If non, do one or more of the following:
-
If the footage is too warped, or distorted, switch the Method to Position, Scale, Rotation.
-
If there are occasional rippled distortions, and footage was shot with a rolling shutter camera, set Advanced > Rolling Shutter Ripple to Enhanced Reduction.
-
Effort checking Advanced > Detailed Assay.
-
-
If the result is too cropped, reduce either Smoothness or Crop Less <-> Smooth More than. Crop Less <-> Smooth More is much more responsive, as information technology doesn't require a restabilize phase.
-
If you desire to get a feel for how much work the stabilizer is actually doing, fix the Framing to Stabilize Only.
When Framing is set to one of the cropping options and the cropping gets extreme, a ruby-red banner appears saying, "To avert extreme cropping set up Framing to Stabilize Only or arrange other parameters." In this situation, y'all tin can either ready Framing to Stabilize But, or Stabilize, Synthesize Edges. Other options include reducing the value of Ingather Less <-> Polish More, or reducing Smoothness. Or, if you are satisfied with the results, enable the Hide Warning Banner option.
Source: https://helpx.adobe.com/after-effects/using/tracking-stabilizing-motion-cs5.html
Posted by: ortegabeent1988.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Change Rotation Point After Effects"
Post a Comment